Break of Structure (BoS) and Change of Character (CHoCH) Trading Strategy
Master the core concepts of BoS and CHoCH to identify key turning points and pattern changes in the market.
Last Updated: May 25, 2025
Trading Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered as financial advice. Trading chart patterns involves substantial risk of loss and is not suitable for all investors. Past performance is not indicative of future results. Always conduct your own research and consider consulting with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
If you’re serious about trading, you already know that chart patterns are one of the key tools in technical analysis. Whether you trade stocks, forex, or cryptocurrencies, understanding and correctly applying chart pattern trading techniques can help you identify trends, pinpoint entry and exit points, and ultimately manage risk more effectively.
In this comprehensive guide, we will take you through a complete chart pattern trading course, from the basics to advanced strategies. We’ll cover every important formation you need to know, including double bottom and double top patterns, bull and bear flags, head and shoulders formations, wedge patterns, triangles, and even cup and handle patterns. This article is designed to provide you with the clarity and actionable strategies you need to trade confidently using chart patterns.
Do you prefer video format? Dive into our full chart patterns trading course on YouTube and improve your technical analysis whether it’s for stocks, forex, crypto, or something else! In this video, you’ll learn how to identify and trade essential chart patterns, like head and shoulders, double tops and bottoms, bull flags, and bear flags.
Chart patterns are visual formations that help traders forecast future price movements across all markets including stocks, forex, and cryptocurrencies
Every chart pattern has two key attributes: direction (bullish or bearish) and type (reversal, continuation, or uncertain)
Reversal patterns like double tops/bottoms and head and shoulders signal trend changes, while continuation patterns like flags and triangles indicate trend persistence
Successful chart pattern trading requires proper risk management with minimum 1:2 risk-reward ratios and strategic stop-loss placement
Volume confirmation and momentum indicators should be used alongside chart patterns to reduce false signals and improve trading accuracy
TradingView Premium automatically identifies chart patterns like double tops, head & shoulders, and triangles across all your charts.
Try Premium Free for 30 Days →Chart patterns are a core component of technical analysis, offering visual clues that help traders forecast future price movements. These patterns emerge from historical price data and tend to repeat across different markets and time frames. By mastering chart patterns, you will be better equipped to:
Identify Trends: Recognize when the market is likely to continue its current trend or when a reversal might occur.
Pinpoint Entry/Exit Points: Determine precise levels for entering or exiting a trade.
Manage Risk: Establish logical stop-loss levels and profit targets based on the structure of the pattern.
One of the key benefits of chart patterns is their universality. They appear in all markets—from stocks to forex to cryptocurrencies—and across various trading styles, whether you’re day trading, swing trading, or scalping. This versatility makes chart pattern trading an essential skill for anyone looking to improve their technical analysis and overall trading performance.
Before diving into specific chart patterns, it’s important to understand how they are classified. Every chart pattern can be described in terms of two main attributes: direction and type.

All chart patterns in trading have a direction and a type. In technical analysis, each pattern is classified by its directional bias, where bullish patterns suggest an upward move while bearish patterns indicate a downward trend, and by its type, such as reversal, continuation, or uncertain.
Bullish Patterns: These patterns indicate that the price is likely to move upward. They are typically observed at the bottom of a downtrend or during periods of consolidation before an upward move.
Bearish Patterns: These patterns suggest that the price is likely to decline. They usually appear at the top of an uptrend or after a period of consolidation before the price falls.

The direction of a chart pattern can be either bullish or bearish and it defines the price direction AFTER the pattern has appeared.
Reversal Patterns: Reversal patterns signal a change in the current trend. For example, a double bottom pattern indicates that a downtrend may be ending and that a bullish reversal is imminent.
Continuation Patterns: Continuation patterns indicate that the prevailing trend will continue after a brief period of consolidation. Bull flags and ascending triangles are classic examples.
Uncertain Patterns: Some patterns, such as symmetrical triangles or broadening ranges, can be ambiguous. They may require additional confirmation to decide whether the trend will resume or reverse.
Understanding both the direction and the type of a chart pattern is essential. It not only helps in identifying the pattern correctly but also in setting up proper trade entries and risk management strategies.
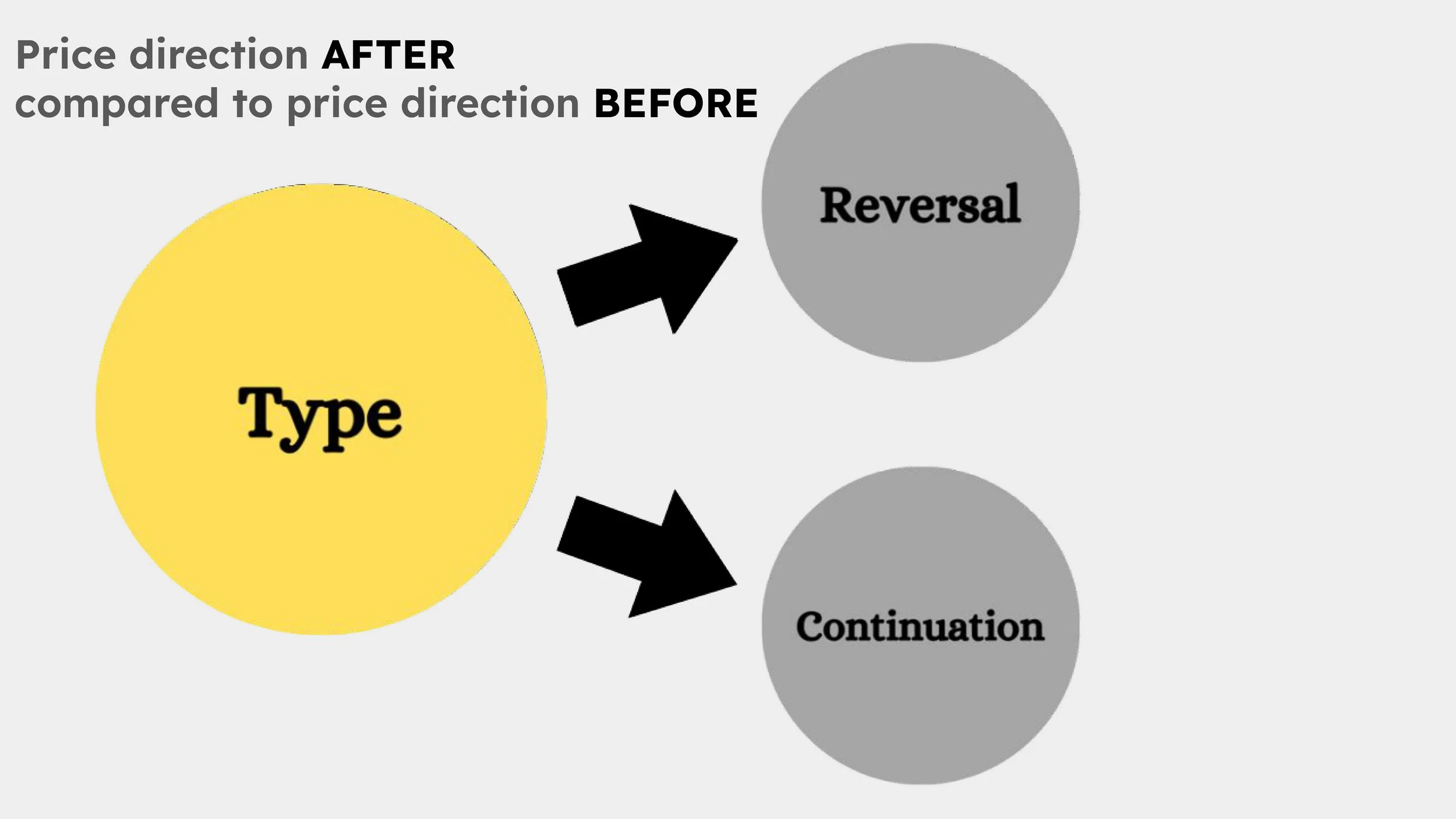
The type of a chart pattern can be classified as reversal, continuation, or uncertain. It describes how the price direction after the pattern compares to the price direction before the pattern formed.
In this section, we take a deep dive into the most important chart patterns. We will explain how to identify each pattern, discuss the underlying logic and psychology, and offer practical trading strategies along with risk management techniques.
Unlock advanced chart pattern recognition, unlimited alerts, and professional trading tools with TradingView Premium.
✔ Claim Your Free TrialThe double bottom is one of the most reliable bullish reversal patterns. It typically appears after an extended downtrend and signals that the selling pressure is subsiding.
Preceding Downtrend: The pattern forms after a sustained decline, making the reversal more significant.
Two Similar Lows: The chart will display two lows that are roughly at the same price level. These lows should be separated by a modest peak.
Intervening Peak: The peak between the two lows forms a resistance level that the price must break through to confirm the reversal.
Entry:
Breakout Entry: Once the price breaks above the intervening peak (the resistance level), consider entering a long position.
Alternate Entry: Some traders prefer entering when the price dips slightly below the initial bounce level and then quickly reverses.
Stop Loss: Place your stop loss just below the lowest point of the pattern to limit potential losses.
Target: A common approach is to aim for a risk-to-reward ratio of 1:2. Measure the distance from your entry point to the stop loss and set your target at least twice that distance.
The double bottom pattern is especially useful for identifying opportunities in various markets, including stocks, forex, and crypto.

The Double Bottom Pattern is a bullish reversal pattern.
The double top is the bearish counterpart to the double bottom and signals that an uptrend may be nearing its end.
Preceding Uptrend: The pattern forms after a significant rise, suggesting that buyers may be running out of steam.
Two Similar Highs: Look for two peaks at similar price levels separated by a moderate trough.
Intervening Trough: The trough between the two highs acts as a support level. When the price falls below this support, the reversal is confirmed.
Entry:
Enter a short position when the price breaks below the support level formed by the trough.
Stop Loss: Place your stop loss just above the higher of the two peaks.
Target: Using a 2:1 risk-to-reward ratio or measuring the distance from the trough to the peaks can help project a reasonable target.
The double top pattern is a clear signal for traders to consider shorting the market, particularly when combined with other indicators.

The Double Top Chart Pattern is a bearish reversal pattern.
The bull flag is one of the most popular continuation patterns used by traders to capture quick profits during an uptrend. It signals a brief consolidation before the price resumes its upward trajectory.
Impulsive Upward Move: A strong, fast-moving upward price move precedes the formation of the flag.
Consolidation Phase: After the initial impulsive move, the price consolidates in a narrow range, forming a flag-like shape.
Trend Resumption: The breakout from the consolidation area indicates that the uptrend will continue.
Entry:
Enter the trade on a breakout above the consolidation range.
Alternatively, wait for a slight pullback to the support level of the flag before entering.
Stop Loss: Set your stop loss just below the lowest point of the consolidation area.
Target: Measure the height of the initial impulsive move and project that distance upward from the breakout point. A risk-to-reward ratio of at least 1:2 is advisable.
Bull flag patterns work effectively in markets that exhibit strong momentum, making them particularly popular among day traders and swing traders alike.

The Bull Flag Pattern is a bullish continuation chart pattern and one of my favorite price patterns due to its simplicity and frequent appearance.
The bear flag is the bearish equivalent of the bull flag. It occurs during a downtrend and signals a brief consolidation before the price continues its decline.
Strong Downward Move: The formation starts with a sharp, impulsive decline.
Consolidation: The price then consolidates in a tight range that resembles a flag, often with a slight upward drift.
Downward Continuation: A breakdown from the consolidation area confirms that the downtrend is likely to continue.
Entry:
Enter a short position as soon as the price breaks below the consolidation area.
Stop Loss: Place your stop loss just above the highest point within the flag.
Target: Determine your target by measuring the initial down move or by maintaining a risk-to-reward ratio of at least 1:2.
The bear flag is a reliable pattern for traders who specialize in selling short, particularly in markets like forex and cryptocurrencies.

The Bear Flag Pattern is a straightforward bearish continuation formation that I also truly appreciate for its clear structure and frequent occurrence in the market.
The head and shoulders pattern is one of the most iconic reversal patterns in technical analysis. It signals that an uptrend is losing momentum and that a reversal to the downside is likely.
Left Shoulder: The formation begins with a peak, which marks the end of an uptrend.
Head: This is followed by a higher peak (the head), indicating a temporary continuation of the uptrend before a reversal.
Right Shoulder: A subsequent, lower peak forms near the level of the left shoulder.
Neckline: Draw a trendline connecting the lows between the peaks. This line serves as a key support level.
Entry:
Consider entering a short position when the price breaks below the neckline. Some traders prefer to wait for a retest of the neckline (which should now act as resistance) before entering.
Stop Loss: Set your stop loss just above the right shoulder.
Target: Measure the vertical distance from the head to the neckline and project that distance downward from the breakout point. A risk-to-reward ratio of at least 1:2 is commonly used.
The head and shoulders pattern is widely respected for its reliability, making it a favorite among professional traders.

The Head and Shoulders Pattern is a classic bearish reversal formation. It is a big chart pattern that often signals a major downturn in price.
The inverse head and shoulders pattern is the mirror image of the head and shoulders. It signals a reversal from a downtrend to an uptrend.
Left Shoulder: The pattern begins with a low point during a downtrend.
Head: A lower low forms next, representing the head.
Right Shoulder: The price then forms a higher low, roughly similar to the left shoulder.
Neckline: Draw a support line connecting the highs between the lows. This line is crucial for confirming the pattern.
Entry:
Enter a long position when the price breaks above the neckline. Some traders wait for a retest of the neckline (now acting as support) before committing.
Stop Loss: Place your stop loss just below the lowest point of the pattern.
Target: Measure the distance from the head to the neckline and project that distance upward from the breakout, or use a minimum risk-to-reward ratio of 1:2.
This pattern is particularly effective for traders looking to capitalize on bullish reversals after a sustained downtrend.

The Inverse Head and Shoulders Pattern is a classic bullish reversal formation. It is a distinctive chart pattern that signals a potential shift from a downtrend to an uptrend.
The falling wedge pattern is unique because it can signal either a reversal or a continuation, depending on the context in which it appears. In a downtrend, it is usually considered a bullish reversal pattern; in an uptrend, it can indicate a continuation.
Converging Trendlines: The pattern is characterized by lower highs and lower lows, with the slope of the highs being steeper than that of the lows.
Narrowing Price Range: As the pattern develops, the price consolidates within a tightening range, signaling potential reversal.
Entry:
Look for a breakout above the upper trendline. Enter on a strong, confirming candle that indicates momentum is shifting.
Stop Loss: Place the stop loss below the lowest point of the wedge.
Target: Measure the height of the wedge and project that distance upward from the breakout level, or use a 1:2 risk-to-reward ratio.
Falling wedge patterns are especially popular among traders who look for early signals of a bullish reversal in a bearish market.

The Falling Wedge Chart Pattern is unique because it can function as both a reversal and a continuation pattern, and in both cases, it signals a bullish trend direction.
The rising wedge pattern, in contrast, is typically a bearish formation when it appears after an uptrend, though it can occasionally signal a continuation in a downtrend.
Converging Trendlines: In this pattern, both higher highs and higher lows are observed, with the upper trendline rising more slowly than the lower one.
Tightening Range: The pattern’s range narrows as time passes, creating a wedge shape that suggests the uptrend is losing momentum.
Entry:
Consider entering a short position when the price breaks below the lower trendline, particularly if a strong bearish candle confirms the breakdown.
Stop Loss: Set your stop loss above the highest point of the wedge.
Target: Use the height of the wedge as a guide to set your target level downward, or maintain a risk-to-reward ratio of at least 1:2.
Rising wedge patterns are valuable for traders looking to short the market after an extended uptrend.

The Rising Wedge Chart Pattern is special as it can function as both a reversal and a continuation pattern. In either case, the Rising Wedge typically signals a bearish trend.
The symmetrical triangle is a classic pattern found in many charts, often representing a period of consolidation before the next move. Although it is typically classified as a continuation pattern, the breakout direction may be uncertain until confirmed.
Converging Trendlines: The pattern forms when the price makes lower highs and higher lows, resulting in converging trendlines.
Balanced Shape: Ideally, the trendlines are nearly symmetrical, although real-market examples often have slight irregularities.
Entry:
Wait for a clear breakout from the triangle. Many traders choose to enter on the candle that closes outside of the triangle’s boundary.
Some traders may also opt for a pullback entry after a false breakout, once the new direction is confirmed.
Stop Loss: Place your stop loss just outside the triangle to protect against false breakouts.
Target: Use the width of the triangle’s base as a measured move to project your target, or set a risk-to-reward ratio of at least 1:2.
Due to the uncertainty associated with symmetrical triangles, using additional indicators for confirmation is often recommended.

The Symmetrical Triangle Chart Pattern can be challenging because its breakout direction is often unpredictable. Personally, I tend to avoid trading this pattern.
The broadening range pattern is one of the more challenging formations to trade due to its inherently uncertain nature. This pattern is characterized by diverging trendlines and increasing volatility.
Diverging Trendlines: In this pattern, the highs continue to rise while the lows continue to fall, creating a fan or megaphone shape.
Increasing Volatility: The widening price range reflects heightened market uncertainty and momentum.
Caution:
Many traders prefer to avoid trading broadening ranges due to their unpredictable nature.
If you do choose to trade, look for a decisive breakout or breakdown and confirm with volume and momentum.
Entry & Stop Loss:
Enter when the price breaks clearly above or below the pattern.
Place your stop loss above the upper trendline (if shorting) or below the lower trendline (if going long).
Target: Because false signals are common, a strict risk-to-reward ratio (such as 1:2) is recommended.
The broadening range pattern serves as a reminder to exercise caution in highly volatile market conditions.

The Broadening Range Pattern, also known as the Megaphone Pattern or Broadening Formation, features diverging trendlines and increasing price volatility, highlighting growing market uncertainty. The pattern is uncertain, and therefore, hard to trade.
The cup and handle pattern is widely recognized for its bullish implications. Although it generally signals a continuation of the uptrend, it can sometimes act as a reversal pattern.
Cup Formation: The cup resembles a U-shaped curve, indicating a period of consolidation after a downtrend or pullback.
Handle Formation: After the cup, the price forms a small consolidation or pullback (the handle) before a breakout.
Breakout: A decisive move above the resistance level (the rim of the cup) signals the continuation of the uptrend.
Entry:
Enter a long position when the price breaks above the handle.
Alternatively, consider entering on a retest of the newly formed support level.
Stop Loss: Place your stop loss just below the lowest point of the handle.
Target: Project your target by measuring the depth of the cup or by employing a risk-to-reward ratio of 1:2 or greater.
This pattern is particularly effective in markets with strong momentum and is a favorite among advanced traders.

The Cup and Handle Pattern is a large bullish continuation formation that typically signals the continuation of an uptrend, though in some cases it can also act as a reversal pattern.
The reverse cup and handle pattern is the bearish equivalent of the traditional cup and handle, indicating that an uptrend is likely to reverse.
Cup Formation: The pattern forms with a U-shaped curve at the top of an uptrend, indicating that prices may have peaked.
Handle Formation: A period of consolidation (the handle) follows the cup, often featuring a rising wedge formation or a tightening range.
Breakdown: The pattern is confirmed when the price breaks below the support level (the rim of the cup).
Entry:
Enter a short position when the price breaks down from the handle.
Stop Loss: Place your stop loss just above the high of the handle.
Target: Measure the height of the cup to determine your target level or use a risk-to-reward ratio of at least 1:2.
This pattern is useful for traders who want to capitalize on bearish reversals following a prolonged uptrend.

The Inverse Cup and Handle Pattern, sometimes called the Inverted Cup and Handle, is a large, typically bearish continuation formation that occurs during a downtrend. It features an inverted cup shape followed by a brief consolidation phase (the handle), indicating that sellers remain in control and the downtrend is likely to continue.
The ascending triangle is one of the most reliable bullish continuation patterns. It is characterized by a horizontal resistance line and rising support levels.
Uptrend Precursor: The market is typically in an uptrend before the pattern forms.
Horizontal Resistance: Multiple tests of the same resistance level occur, creating a clear horizontal line.
Rising Lows: The lows gradually rise, indicating increased buying pressure.
Entry:
Enter a long position when the price breaks above the horizontal resistance line.
Stop Loss: Place your stop loss just below the most recent higher low.
Target: Use the vertical distance between the resistance line and the support line as a measured move, or maintain a risk-to-reward ratio of 1:2.
Ascending triangles are favored by traders for their clarity and reliability, especially in trending markets.

The Ascending Triangle Pattern is a bullish continuation formation that clearly indicates increasing buying pressure in an established uptrend. It's one of my favorite chart patterns due to its clarity and reliability.
The descending triangle is essentially the bearish counterpart to the ascending triangle. It signals that the downtrend is likely to continue after a period of consolidation.
Downtrend Precursor: The market is in a downtrend when this pattern forms.
Horizontal Support: The support level remains relatively flat, even as the highs continue to decline.
Falling Highs: The upper trendline slopes downward, indicating increasing selling pressure.
Entry:
Enter a short position when the price breaks below the horizontal support level.
Alternatively, wait for a pullback after the initial breakdown for added confirmation.
Stop Loss: Place your stop loss just above the most recent lower high.
Target: Measure the distance from the support level to the high or set a risk-to-reward ratio of at least 1:2.
Descending triangles offer a clear setup for traders looking to sell into a weakening market.

The Descending Triangle Pattern is a bearish continuation formation that clearly indicates mounting selling pressure within an established downtrend. It forms as the price repeatedly tests a horizontal support level while making lower highs, signaling that the downtrend is likely to persist. I favor this pattern for its clear structure and reliable indication of continued bearish momentum.
Beyond simply identifying chart patterns, successful trading lies in the implementation of effective strategies and disciplined risk management. Here are some practical tips to enhance your chart pattern trading approach:
Breakout Entries:
Enter trades when the price decisively breaks through a key support or resistance level.
Ensure that the breakout is supported by increased volume and strong momentum to reduce the likelihood of a false signal.
Pullback Entries:
Alternatively, wait for the price to retrace slightly after the initial breakout.
This strategy often results in a better risk/reward setup by providing a tighter entry and stop-loss placement.
Proper Stop Loss Placement:
Use the structure of the pattern to set your stop loss. For instance, place it below the bottom of a double bottom or above the top of a double top.
Risk-to-Reward Ratio:
Aim for a minimum risk-to-reward ratio of 1:2. This means that the potential profit should be at least twice the amount you risk on the trade.
Adjusting Positions:
As your trade moves in your favor, consider trailing your stop loss to lock in profits.
Volume Analysis:
Confirm breakouts with increased trading volume, which adds validity to the pattern.
Momentum Indicators:
Use additional indicators such as RSI or MACD to further confirm the strength of the move before entering a trade.
Backtesting:
Review past charts and practice identifying patterns to build confidence and refine your approach.
Simulated Trading:
Consider practicing with a demo account to gain practical experience before committing real capital.
Keep a Trading Journal:
Document your trades, including your rationale and outcome. This helps in identifying strengths and areas for improvement.
Flexibility:
Not every chart pattern will play out perfectly. Adjust your strategy based on the market’s unique characteristics and current volatility.
Combining Patterns:
In many cases, chart patterns work best when combined with other technical analysis tools. For example, using trendlines, support/resistance levels, and candlestick patterns can help refine entry and exit decisions.
Discipline:
Stick to your trading plan and avoid chasing trades outside your strategy.
Patience:
Allow patterns to fully develop before making your move. Rushing in too early can lead to poor risk management and potential losses.
By following these strategies and continually refining your approach, you can become more consistent and successful in your chart pattern trading.
Chart pattern trading is both an art and a science. When you understand the technical aspects behind each formation and the psychology that drives market behavior, you are in a far better position to make informed trading decisions. Whether you’re working with a double bottom pattern, a head and shoulders formation, or any other chart pattern, the key to success lies in continuous practice, disciplined risk management, and an adaptive strategy.
This guide has provided you with an in-depth look at a wide variety of chart patterns—from the bullish double bottom and ascending triangle patterns to the bearish double top, head and shoulders, and descending triangle patterns. Each pattern offers unique insights into market behavior, and when applied correctly, they can significantly improve your trading performance across different financial markets, including stocks, forex, and cryptocurrencies.
Remember that no strategy is foolproof, and not every pattern will result in a successful trade. The goal is to use these patterns as tools in your overall trading toolkit—combined with other forms of technical and fundamental analysis—to help you make smarter, more informed decisions.
If you’re new to chart pattern trading, start by practicing on historical charts and gradually move into live trading once you’re confident in your ability to read and react to these patterns. With time, patience, and continuous learning, you will develop the discipline and insight needed to navigate even the most challenging markets.
We hope you find this comprehensive chart pattern trading course valuable. By integrating these concepts into your trading routine, you’ll be well on your way to mastering technical analysis and achieving consistent profitability.
Happy Trading, and may your charts always guide you to success!
Pro Tip: Want to identify chart patterns automatically? TradingView Premium scans all markets for patterns like double tops, triangles, and flags in real-time. Get 30 days free + $15 bonus →
The double bottom and double top patterns are often considered the most reliable for beginners due to their clear structure and straightforward trading rules. They offer distinct entry points, stop-loss levels, and profit targets.
Chart patterns can form over various timeframes, from minutes on intraday charts to months on daily or weekly charts. The key is to match your pattern analysis with your trading style and time horizon.
While chart patterns can be traded alone, combining them with volume analysis, momentum indicators (like RSI or MACD), and support/resistance levels significantly improves accuracy and reduces false signals.
Reversal patterns signal a change in the current trend direction (like head and shoulders or double tops), while continuation patterns indicate the trend will resume after consolidation (like flags, pennants, and triangles).
Volume is crucial for confirming pattern breakouts. A genuine breakout should be accompanied by increased volume, while breakouts on low volume are more likely to fail. Always check volume before entering a trade.
Master the core concepts of BoS and CHoCH to identify key turning points and pattern changes in the market.
Learn to identify key price levels that form the foundation of chart patterns and market structure.
Master multi-timeframe analysis to improve your chart pattern recognition and trading accuracy.
Discover how to identify swing points that form the basis of most chart patterns and trend analysis.
Trading & Investing Enthusiast
Teaching traders to understand market psychology, technical analysis, and investing through clear beginner-friendly insights.
Started investing at 16 and became fascinated by how market psychology influences price movements. Still learning something new every day.
Love sharing what I've learned along the way. There's nothing quite like helping someone understand a concept that once confused me too.
Proud to have built a community where traders actively share insights and grow together through daily market analysis and discussion.
Want to join our learning journey?