How to Draw Fibonacci Retracement Correctly in TradingView
Master Fibonacci retracement levels to identify optimal pullback entry points with precision.
Last Updated: December 11, 2025
Pullbacks—also known as retracements or consolidations—are an essential concept in trading. In this guide, we’ll dive into what pullbacks are, the key characteristics to look for, and strategies for trading both simple and complex pullbacks effectively. Whether you're in forex, crypto, or stock trading, mastering pullback trading strategies can enhance your decision-making and profitability.
For visual learners, watch the full video “Best Pullback Trading Strategy (Simple or Complex?)” here.
Recognize pullbacks as temporary counter-trend moves—characterized by smaller candles, mixed colors, and multiple wicks—that signal a pause before the primary trend resumes.
A simple pullback is a clean, single reversal, while a complex pullback involves multiple counter moves—mastering both types can unlock valuable trading opportunities.
Combine trend identification with technical indicators such as moving averages, Fibonacci retracement, and candlestick patterns to pinpoint optimal entry points after a pullback.
Always wait for confirmation that the pullback is ending before entering a trade—look for strong candles resuming the primary trend direction.
Enhance your pullback strategy with robust risk management and leverage platforms like TradingView to visualize and validate market conditions.
A pullback is a temporary reversal that goes against the current trend. Think of it as a pause in a trend—a moment where price moves in the opposite direction before potentially continuing in the original trend’s direction. For instance, during an uptrend, you might see a brief move downwards; this is the pullback.
Consider a market where the price moves upwards with strong momentum (known as the impulsive move). After this move, a brief consolidation or minor reversal occurs before the trend resumes. This minor reversal against the primary trend is the pullback.
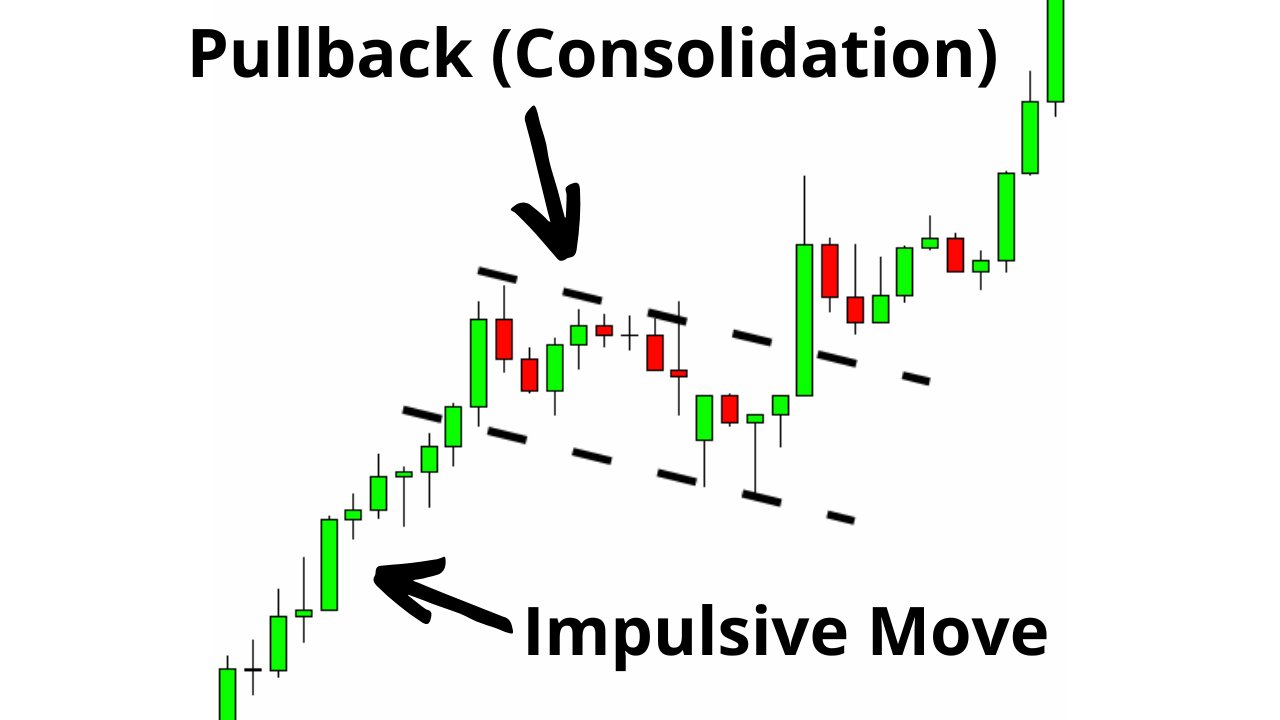
What is a Pullback in Trading? A pullback is a brief, counter-trend movement within an ongoing trend, providing a temporary pause before the trend potentially resumes.
Identifying a pullback accurately is critical. Here are some indicators to help you spot them:
Pullbacks often have small candle bodies compared to the previous impulsive move. It normal to find spinning top and doji candles within the pullback.
Example: In an uptrend, if the initial move shows large green candles, a pullback might show smaller, mixed-color candles.
Look for candles of different colors (e.g., both red and green in an uptrend).
This indicates a pause in the trend, with buying and selling pressure balancing temporarily.
Pullbacks often show multiple wicks—both upper and lower—indicating price indecision.
Large wicks on either side of a candle body signal potential reversals within the pullback.
Use this checklist while analyzing your charts to confirm a valid pullback
Understanding the difference between simple and complex pullbacks is essential for refining your trading strategy. Here’s a breakdown:

Complex vs Simple Pullbacks in Trading: A simple pullback shows a single, straightforward counter-trend move, while a complex pullback contains multiple counter-trend moves, creating a minor trend within the pullback.
A simple pullback involves a single counter-trend move. This looks like a clean, straight retracement in the opposite direction, followed by a continuation of the original trend.
Example: In an uptrend, the price makes a minor, straight-line dip before resuming the upward momentum.
Complex pullbacks have multiple counter-trend moves within them. Instead of a single reversal, a complex pullback forms a structure with minor highs and lows within the overall pullback.
Example: In an uptrend, instead of a single dip, the price might move down, then up slightly, then down again, creating a miniature downtrend within the pullback.
Why Trade Complex Pullbacks? While they are more challenging to spot, complex pullbacks offer high reward potential. Once mastered, they provide solid opportunities for strategic entries and exits.
✅ Best for: New traders learning pullback basics
🎯 Best for: Experienced traders seeking higher returns
Pro Tip: Start by mastering simple pullbacks. Once you can consistently identify and trade them, progress to complex pullbacks for greater profit potential.
Pullbacks offer prime entry opportunities in trending markets. Here’s a pullback trading strategy to consider:
Confirm the primary trend direction (uptrend or downtrend).
Use a tool like TradingView to visualize and analyze trends accurately. (Using my affiliate link can help support this blog!)
Learn about concepts like market structure and price action for more accurate trend analysis.
In an uptrend, wait for a minor reversal or consolidation that suggests a pullback.
Look for smaller candles, mixed colors, and multiple wicks.
Once the pullback shows signs of ending (e.g., a strong candle resuming the primary trend), consider entering the trade.
For serious traders, tools like InvestingPro can help monitor economic data and market sentiment, supporting your decision to enter or exit based on trend direction.
Knowing when to enter during a pullback can make or break a trade. Here are some common strategies:
In an uptrend, you might wait for the pullback to reach a key moving average line (e.g., 20-day or 50-day). If it bounces from there, this can signal a good entry point.
In downtrends, look for the pullback to reach the moving average from below, suggesting a resistance level.
Important: Using moving averages as support and resistance has its limitations, and it’s a strategy I generally avoid. However, I’m including it here because it’s widely used and many traders claim to find success with it.
Use Fibonacci levels to identify possible support or resistance during pullbacks. Common retracement levels include 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8%.
Enter when the price respects a Fibonacci level and shows signs of resuming the trend.
Look for reversal patterns like engulfing candles, doji candles, or hammer patterns as confirmation to enter after a pullback.
Ensure the pattern aligns with the primary trend direction to increase the chance of success.
Understanding and mastering pullbacks can make your trading strategy more resilient and adaptable. By recognizing the key characteristics of pullbacks and differentiating between simple and complex types, you’ll be better equipped to seize trading opportunities confidently.
Master Fibonacci retracement levels to identify optimal pullback entry points with precision.
Learn to identify trends, reversals, and continuation patterns—the foundation for spotting pullbacks.
Understand swing points to identify where pullbacks begin and end within a trending market.
Use moving averages as dynamic support and resistance to time your pullback entries.
Trading & Investing Enthusiast
Teaching traders to understand market psychology, technical analysis, and investing through clear beginner-friendly insights.
Started investing at 16 and became fascinated by how market psychology influences price movements. Still learning something new every day.
Love sharing what I've learned along the way. There's nothing quite like helping someone understand a concept that once confused me too.
Proud to have built a community where traders actively share insights and grow together through daily market analysis and discussion.
Want to join our learning journey?
Tools I use to spot retracements and time trend continuations